Different Sycamore Trees: Types, Varieties & Species
Majorly there are eight types of Sycamore that are most prevalent. Learn about each of them in detail below.
Sycamore is a deciduous tree, which is a favorite amongst many cultures. Belonging to the Platanus genus, they are also called plane trees in North America. It is a prevalent shade tree that grows between seventy and eighty feet, sometimes even higher. They have a deep root system, making them robust.
Sycamore also has a wide spread. Hence, demand a good space to grow. You can conveniently spot them lining streets or in the parks. The fast-growing tree develops more than two feet annually. But did you know how many different types of sycamore trees exist?
Broadly, there are eight sycamore types. Six of them are native to North America. Most varieties are majestic and large with a far-spreading canopy, white bark exfoliating to reveal the darker patches, and large lobed deciduous leaves.
Some even classify the sycamores into two categories. First is the ornamental hardwood that lives for over a century and towers over other trees. The other is the fig-producing variety prevalent in the Middle East.
Sycamore Tree Identification Overview
| Scientific name | Platanus occidentalis |
| Other common names | American Sycamore, Buttonball Tree, Buttonwood, Western Planetree, American Planetree |
| Native to | Eastern and the central United States |
| Type (deciduous or evergreen) | Deciduous |
| Flower | Monoecious small flowers that grow in densely round clusters |
| Seeds | The tree matures in brownish, small balls annexed to the branch. These balls are not a single fruit but a bundle of several tiny spiked seed-like fruits known as achenes. |
| Fruits | Achenes, dry spheres that retain their seeds |
| Bark | Mottled, peeling bark that gives the tree a scabby look |
| Leaf | Large, light-green leaves that resemble maple leaves |
| Growth rate | Two feet per year |
| Mature Size (height & spread) | 75–100 ft. tall, 75–100 ft. wide |
| Lifespan | Over 250 years |
Different Types of Sycamore Trees
Now let us discuss the most commonly found Sycamore trees one by one.
1. American Sycamore Tree
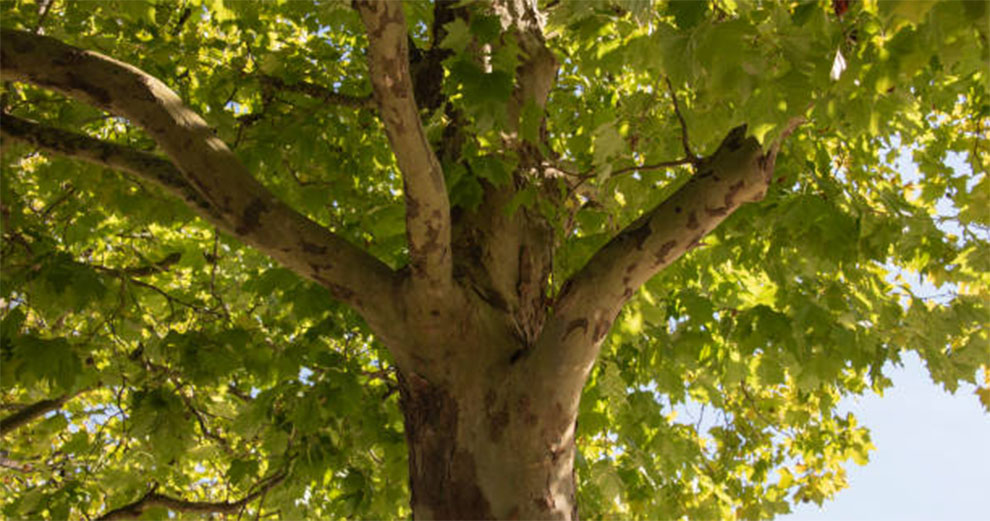

Botanically called the Platanus occidentalis, the American Sycamore tree has a vast coverage area and grows up to 100 feet tall. However, sometimes, it might even grow up to 170 feet tall.
Native to the eastern part of America, the American Sycamore tree is a true Sycamore and is also called Eastern sycamore, occidental plane, buttonball, and buttonwood. It is called the buttonball because of its button ball-shaped fruit clusters.
Some of the specimens live for over four centuries. Primarily people grow these sycamore tree species as shade trees in the city. You can spot them in USDA hardiness zones 4b through 9a.
They can tolerate different soil types but thrive in rich, moist, and well-draining soils. However, these long-liked species have destructive roots that may damage the roads or sidewalks.
2. California Sycamore Tree
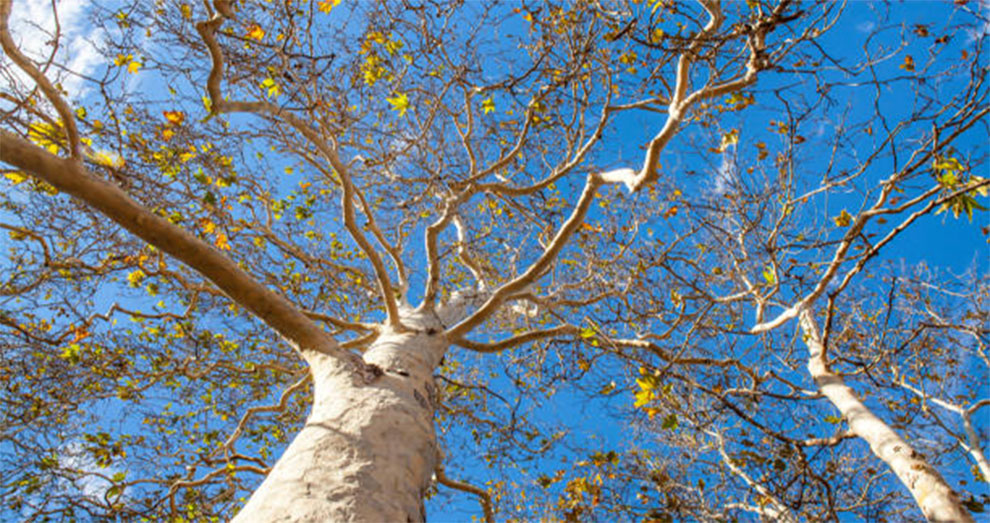

It is one of the taller sycamore trees that grows up to 110 feet. California Sycamore resembles American Sycamore in appearance and growth. Botanically called the Platanus racemose, California Sycamore Tree is prevalent on the western coast of the United States.
Many even refer to it as the Western Sycamore or California plane tree. The plant thrives in USDA hardiness zones seven through ten. It is a fast-growing tree, growing more than two feet per year, and a graceful tree with a leaning habit.
People usually plant it in California as a landscape and a street tree. It offers food, shelter, and nesting sites to wildlife, such as woodpeckers, hawks, owls, songbirds, and hummingbirds. These types of sycamore trees thrive in unfiltered and direct sunlight for six hours every day.
3. Arizona Sycamore Tree
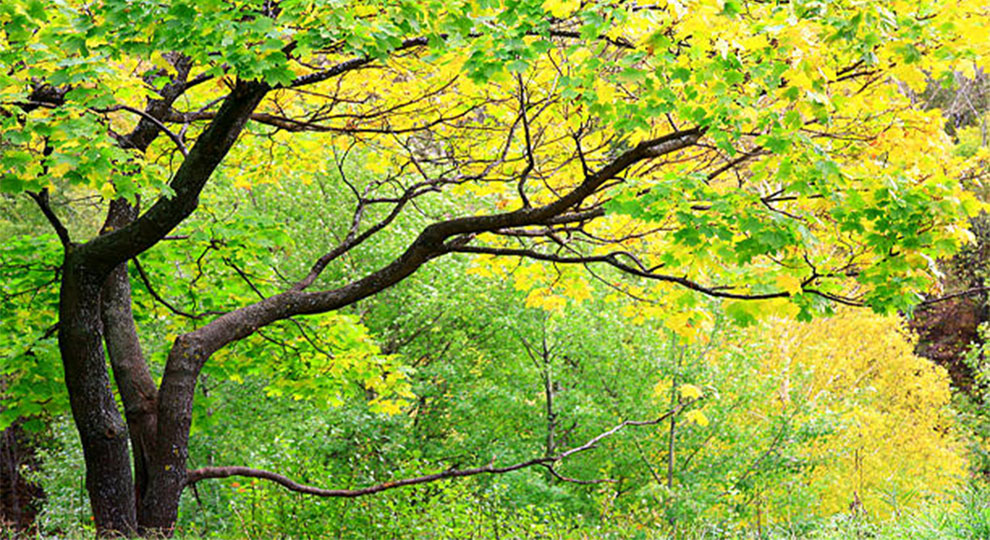

Native to Mexico and Arizona, Arizona Sycamore is a deciduous tree that grows up to eighty feet with an equal spread. Botanically called the Plantanus Wrightii, Arizona Sycamore trees are native to deserts of the United States.
Compared to the other varieties, it is not as drought-resistant. Hence, it will demand a regular water supply. It grows best in USDA hardiness zones seven through eleven, especially near streams and rivers.
However, you can also spot it in vast private or public spaces like farms, parks, or gardens. But, because of its majestic size and aggressive growth habit, it is not ideal for residential places.
It has a stiff and upright habit sans symmetry. Many botanists refer to the Arizona Sycamore tree as the California sycamore subspecies. But, they are highly anthracnose resistant as opposed to the California sycamores.
4. London planeSycamore Tree

It is one of the hybrid types of sycamore trees. The tree is an amalgam of the Oriental plane (Platanus orientalis) and American sycamore (Platanus occidentalis). Botanically called the Platanus x hispanica Sycamore tree, the London plane is also called the English Sycamore.
Like most Sycamores, these trees also develop clusters of small flowers in crimson-red and yellowish-green colors. Its red flowers are female variants, and the yellow ones are male.
London Plane is also a vast spreading tree used as a shade tree. It grows to eighty to hundred feet tall if the conditions are favorable. The plant thrives best in USDA hardiness zones five through nine with regular irrigation.
It is tolerant of urban conditions like compacted soil and pollution. London Plane has a durable and strong wood used for various purposes like flooring and furniture.
5. MexicanSycamore Tree

Botanically called the Platanus Mexicana, the Mexican Sycamore is a deciduous tree prevalent in parts of Texas. Native to Northeastern and Central Mexico, you will also find these sycamore tree varieties in Florida.
Compared to the American Sycamore, they are relatively smaller and grow between forty and fifty feet. However, some might go up to eighty feet with a trunk having a two-meter diameter.
These trees usually grow thirty-six inches per year. Even though the American sycamore trees are susceptible to diseases like bacterial leaf scorch, the Mexican ones are more resistant.
Since they are smaller in structure than the American Sycamore, they are more likely to be seen in neighborhoods. Regardless, they are still considered large trees with aggressive and deep roots. Hence, plant them near pavements or homes.
6. Old world Sycamore Tree

These giant sycamore varieties grow up to 100 feet high. Also called the Oriental planetree, they are native to the Middle East and the eastern part of Europe. Even though the plant thrives in damp conditions, it can also withstand drought.
These deciduous trees have a long lifespan and tend to have a spreading habit. Their leaves are large and thick and grow about ten inches wide with a maple-like leaf appearance.
These sycamore tree species have a dark to medium green shade with five to seven lobes and serrated edges. You can also find deep notches in between the lobes. The green leaves change their color to yellow, red, or amber during the fall.
Its bark is rugged and thick with color that is all shades of grey and brown that flakes off to display the white patches. The bark exfoliation commences only once the tree matures.
Honorary Mention!
Sycamore Maple Tree

It is a deciduous tree with a medium texture. Botanically called the Acer Pseudoplatanus, they are majestic and wide trees. Also referred to as the Plane Tree Maple, they are native to Europe.
Their branches have a spreading habit and are usually compact and dense. The trees grow about forty to sixty feet tall, but some varieties might even grow up to 110 feet.
Sycamore Maple trees have an oval to rounded shape with leatherlike, thick, green leaves about three to six inches wide. The leaves are green on the top but tinged with white on the underside.
Its flowers are yellowish green and usually, show in May. It is not from the true sycamore tree varieties. It is a Maple tree that is called Sycamore because of its features. However, it belongs to the Acer family. Their pendulous-shaped fruits show in clusters about two inches wide.
These thrive in full sun conditions, especially in USDA zones four through seven. They grow well in acidic soil with full sun to light shade conditions. Overall, these are one versatile variety.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ques 1. What is the difference between American Sycamore and Mexican Sycamore?
Ans. Even though American Sycamore and Mexican Sycamore look similar, they have some differences in them. Below we will address the common differences between American Sycamore and Mexican Sycamore:
- Both belong to the Platanus genus and have almost similar leaves and flowers. Platanus Occidentalis or American Sycamore hails from Eastern North America, but the Platanus Racemosa, or Mexican Sycamore, originates from Central Mexico.
- American sycamore species are taller than Mexican sycamores. It is a deciduous tree that grows up to one hundred and twenty feet tall. They live for about two centuries.
On the other hand, the Mexican Sycamore is a cold-hardy, fast-growing plant that grows up to seventy-five feet. Native to North America, you can find them across Europe.
- Mexican Sycamore has a rough, brown or gray, smooth bark with a lacy texture. American Sycamore has vertical grooves running along its smooth bark that appear as if there are large scales on the surface.
- American Sycamore has compound leaves with seven or five leaflets each, with serrated edges. Its leaves are dark green and large with a waxy surface, creating a smooth appearance while young. As the leaves grow older, they dry out.
Mexican Sycamore has relatively smaller leaves. But they do have a waxy surface like their American counterparts.
Ques 2. What is special about sycamore trees?
Ans. The varieties of sycamore trees have an illustrious history in folklore that travels back to ancient Egyptians when the Holy Sycamore was considered a conduit bridging and connecting the abyss, which distinguishes the dead and the living.
It was considered one of the most handsome trees by the Persians and ancient Greeks. Hence, they planted it everywhere. Sycamore has several medicinal qualities and has long been used for homeopathic remedies.
Its inner bark works as a disinfectant. Moreover, it has also been used to cure everything from rashes to coughs and arthritis pain.
What’s more?
The wood from the tree also has multiple applications. People employ it for wine barrels, barber poles, cartwheels, shelves, butcher blocks, flooring, different furniture, violin backs, interior trim, and paneling.
French traders and Native Americans constructed canoes from sycamore lumber. The Sycamore is resilient and sturdy.
They relish the snow, grow in cold regions, love the sun, and need minimum to survive for centuries. Hence, it is the best offset tree if planted in its native habitat and shielded by carbon offset companies working to remove carbon footprint from the emissions.
Ques 3. What is the lifespan of a sycamore tree?
Ans. The sycamore species can live for over four centuries.
Ques 4. Which pests and diseases affect the sycamore tree?
Ans. Sycamore trees are susceptible to several diseases and pests. However, with the proper Sycamore care, you can keep the plant healthy.
Some prevalent problems that may hamper the plant’s growth are scale insects, aphids, borers, powdery mildew, leaf miner damage, caterpillars, and Verticillium wilt.
