How Fast Do Tulip Trees (Yellow Poplars) Grow?
Tulip trees have a slow to moderate growth rate. The initial and after-maturity days are relatively slower as compared to the midway growth period.
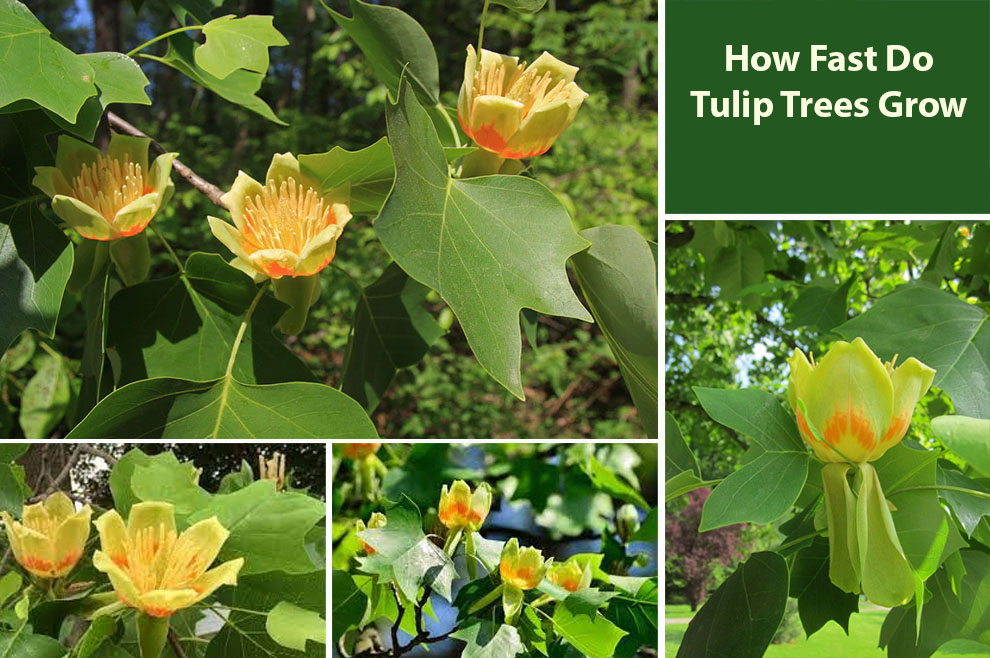
Also called the Liriodendron tulipifera, Tulip trees are slow-growing and majestic. However, they may exhibit a varying growth rate depending on your planted variety.
But if you precisely ask us how fast do tulip trees grow? When will it flower? Can I do something to make it grow quickly?
Let us tell you, ideally, in their initial growth years, tulips depict a notably slow growth rate as they gradually develop over time. This slow growth rate is because of their long maturation period. They take around two decades before they attain complete maturity.
| Did You Know!
The ‘Tulip tree’ also known as the Yellow Poplar tree is not the same as the flower ‘Tulips.’ These trees actually belong to the Magnolia Family. |
The growth rate of tulip trees can vary, but on average, it is moderately between two to three feet per year during its active growth phase. This is the time when the initial slow growth phase is over.
This measure of growth rate allows you to help the tree to develop a robust and sturdy structure as it matures. They can reach a maximum height of between 80 – 100 feet.
As the tulip trees reach their full height, they display their magnificent blooms for an extended duration, accentuating their beauty and allure.
With their patient growth trajectory, the tulip trees exemplify the golden adage that good things come to those who wait. Tulips’ slow yet steady growth allows for the development of a remarkable tree that brings grace and grandeur to its surroundings.
Tulip Tree Information
| Common names | Tulip tree, Yellow poplar, Tulip poplar, Whitewood |
| Annual growth rate | 2-3 feet per year |
| Mature tree size | 80 – 100 feet in height, with a spread of 35-50 feet |
| Tulip tree lifespan | Typically around 100-150 years |
| Bloom time | Late spring to early summer |
How Fast Do Tulip Poplar Trees Grow Each Year?
As stated, tulip trees have a slow to moderate growth rate. They add between two to three and rarely five feet to their height each year.
While the exact growth rate may vary with factors like climate, soil conditions, and the tree’s overall health, this range gives a general estimate for their annual growth.
As slow-growing trees, it takes tulips several years to reach their mature height, which usually ranges from 80 to 100 feet.
However, their gradual growth rate allows them to develop a sturdy and robust structure, ensuring their longevity and ability to endure different environmental conditions.
With their vibrant tulip-like flowers and elegant shape, tulip trees captivate observers as they steadily rise toward the sky.
Related: Japanese Magnolia Varieties | Different Types of Magnolia Trees
Growth Stages of Tulip Trees
Tulip trees go through distinct growth stages – seed germination and early growth, establishment and juvenile growth, rapid growth phase, and maturation and slowing growth.
Below we will discuss them in detail:
A. Tulip tree seed germination and early growth
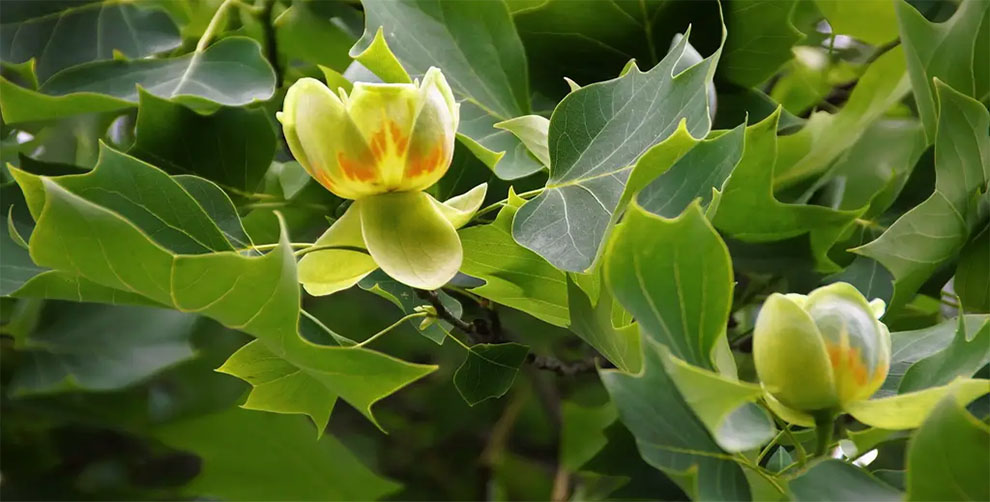

During the early growth stage and seed germination, the tulip trees commence their journey. It starts with the seed that requires specific conditions to sprout. This takes 60-90 days to break the dormancy and germinate.
Once the seed germinates, a young seedling shows from the soil. The seedling is vulnerable and delicate at this stage, relying on moisture and ample sunlight to develop. It dedicates its energy to establishing a robust root system and yielding the initial set of true leaves.
It is a crucial stage for the seedling to gather resources and develop a foundation for future growth. The tulip tree seedling advances to the next phase and showcases excellent results, provided it receives favorable conditions and proper care.
B. Tulip tree establishment and juvenile growth
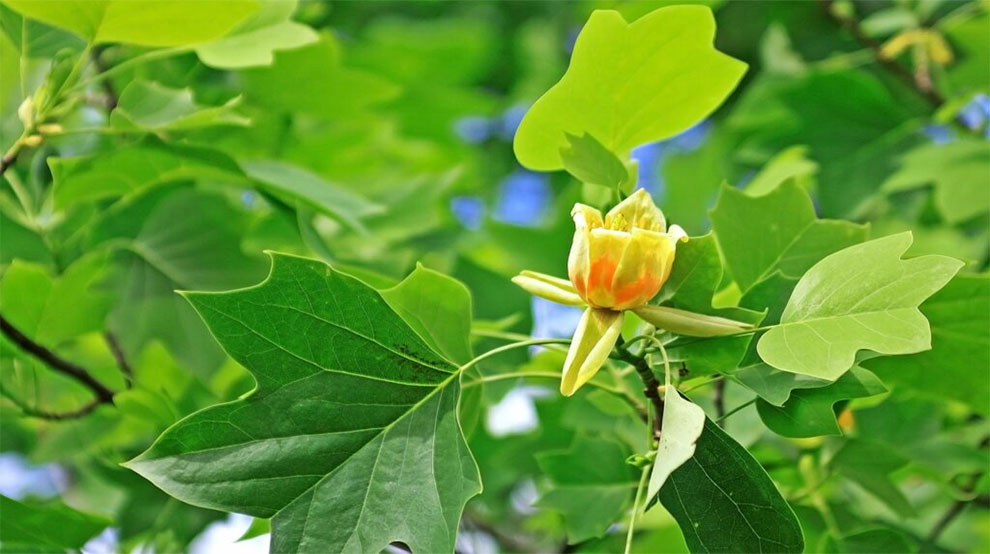

In the juvenile growth and establishment stage, the tulip tree seedling metamorphoses into a young tree. This stage is characterized by significant development as the tree develops a root system and grows in girth and height.
The yellow poplar growth rate is rapid when the tree enters the juvenile phase. Consequently, the tree endures substantial vertical growth and adds several feet to its height every subsequent year.
Furthermore, it also increases in diameter as it expands its branches and trunks. This growth is supported by the tree’s ability to capture sunlight efficiently and convert it into energy via photosynthesis.
At this stage, the tulip tree directs its vitality towards building resilience and strength to prepare for the challenges that it may endure in the future. Hence, it invests most of its energy into growing branches and leaves that offer an increased surface area to capture sunlight and facilitate photosynthesis.
With favorable conditions and proper care, the tree advances into the next phase of its life cycle, characterized by even more rapid growth and eventual maturation.
C. The rapid growth phase of Tulip tree

It marks a significant period of development and expansion for the tulip tree. As part of this stage, the tree undergoes considerable growth in girth, canopy spread, and height.
With a sturdy trunk and an established root system, the tulip tree channels its energy toward vertical growth. Hence, it reaches notable heights every year.
In the rapid growth phase, the tree’s branches extend outward, filling the canopy and offering ample space for the leaves to capture sunlight.
It aids in further photosynthesis and efficient energy conversion for growth. The tree’s trunk thickens, providing structural stability and support to accommodate its increasing size.
Under optimal conditions, the tulip tree grows several feet during this phase, expanding its presence in the landscape. It depicts a spectacular ability to respond and adapt to the environment, leveraging the available resources to fuel its rapid growth.
As the tulip tree experiences this accelerated growth, it becomes an impressive sight, commanding attention with its lush foliage and towering height. This phase signifies the tree’s vitality and vigor as it matures to its 100% potential.
D. Maturation and slowing growth

In this stage, the tulip tree reaches the pinnacle of development. Hence, it exhibits a more measured growth rate. After acquiring a considerable size and height, the tree directs its resources toward optimizing resource allocation and strengthening its structure.
In this stage, the tulip tree’s growth rate gradually declines compared to all three previous phases. Now the plant shifts its focus from vertical growth to form refinement and more on lateral expansion.
Of course, the tree does not curtail the canopy development, as it is vital for photosynthesis and producing energy.
While the tulip might still experience some growth in girth and height, it manifests at a significantly reduced pace. The focus shifts towards preservation and maintenance as the tree dedicates its resources to fortifying the branches, trunk, and root system.
At this point, the tree puts all its energy towards its seeds and flowers, contributing to its reproductive cycle.
Factors Affecting How Fast Do Tulip Poplars Grow
You must also understand that multiple factors have a role in influencing tulip poplar growth rate.
Climate and environmental conditions, soil quality and nutrition, sunlight exposure, and water availability all contribute to a tree’s overall growth and development. Let us see how each one of these has a role to play.
A. Climate and environmental conditions
Environmental and climatic conditions significantly impact the yellow poplar trees’ growth rate. Tulips thrive in temperate regions. They cherish moderate to mild climates and like areas with well-distributed year-round rainfall.
However, they are sensitive to frost, drought, and extreme temperatures. Optimal growing conditions include a sufficient amount of precipitation and moderate average temperature.
Adverse climate conditions cause stress, hinder growth, and stunt the plant’s growth. Factors such as exposure to pollutants, strong winds, and temperature fluctuations prove detrimental to the tulips.
B. Soil quality and nutrition
The soil and nutritional quality also have a role in determining the yellow poplar tree’s growth rate. These trees thrive in well-drained soil with a good organic matter compost and loamy texture.
Adequate soil nutrition is imperative for the tree’s overall growth and health. Essential nutrients, like potassium, phosphorous, and nitrogen, are vital for optimal development and growth.
Insufficient nutrient availability causes weakened tree health, reduced foliage, and stunted growth.
Furthermore, soil pH levels influence nutrient availability. Tulips cherish a slightly acidic to neutral soil. Ensuring superior soil quality and appropriate nutrient supplementation fosters healthy root development and supports the vigorous growth of yellow poplar trees.
C. Sunlight exposure
Sunlight is another essential factor that significantly affects the yellow poplar tree growth rate . They thrive in partial shade to full sun conditions.
Moreover, insufficient sunlight exposure leads to elongated stems, sparse herbage, and weaker branches.
On the contrary, with ample sunlight, Tulip trees promote sturdy branching, vigorous growth, and abundant foliage. Thus, you must ensure your plant receives adequate sun across the day to maximize its growth potential and maintain vitality.
D. Water availability

Water availability is a vital factor that directly affects tulips’ growth rate. Yellow Poplar needs a consistent and adequate water supply to support their growth and development.
Inadequate water can result in water stress, manifesting as leaf wilting and reduced growth. But an ample water supply ensures proper hydration, facilitating photosynthesis and nutrient uptake.
The absence of adequate water, especially during critical growth periods, hinders root development and curtails the plant’s ability to absorb vital nutrients.
Optimal water availability helps promote healthy foliage and a robust root system and aids in overall growth. Hence, monitoring water levels and regular irrigation is crucial to ensure sufficient hydration for sustained growth.
